Introduction to Nutrition
Nutrition is the science that studies the interactions between living organisms and the elements of food they consume. It is fundamental to human health, playing a pivotal role in maintaining bodily functions and overall well-being. Nutrients, the substances in food that our bodies need to function properly, are categorized into macronutrients and micronutrients.
Macronutrients include carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, which are required in larger amounts and provide the energy necessary for bodily processes. Carbohydrates are the primary source of energy, proteins are essential for growth and repair of tissues, and fats are crucial for absorbing vitamins and providing long-term energy storage. Micronutrients, on the other hand, are vitamins and minerals needed in smaller quantities but are equally vital for health. They support various physiological functions, including immune response, bone health, and cellular metabolism.
A balanced diet, which includes an appropriate mix of macronutrients and micronutrients, is essential for maintaining optimal health. Consuming a variety of foods ensures that the body receives all the necessary nutrients it requires. Conversely, poor nutrition can lead to a range of health issues. Malnutrition, whether it is undernutrition or overnutrition, can result in serious health problems. Undernutrition occurs when there is a deficiency of essential nutrients, leading to weakened immunity, stunted growth, and increased susceptibility to diseases. Overnutrition, often due to excessive intake of certain types of foods, can lead to obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and other diet-related conditions.
Understanding the principles of nutrition helps individuals make informed dietary choices, promoting a healthier lifestyle and preventing nutrition-related diseases. As we delve deeper into the types, uses, and consumption strategies of nutrients, it becomes evident that nutrition is not just about eating but about nourishing the body in a way that supports its myriad functions.
Types of Nutrition
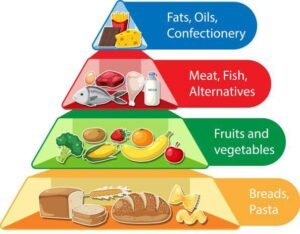
Understanding the types of nutrients essential for our bodies is fundamental to maintaining optimal health. Nutrients can be broadly categorized into macronutrients and micronutrients. Each type plays a distinct role in bodily functions and overall well-being.
Macronutrients

Carbohydrates: Carbohydrates are the primary source of energy for the body. They are broken down into glucose, which fuels cellular activities. Common sources of carbohydrates include fruits, vegetables, grains, and legumes. The recommended daily intake varies based on age, sex, and activity level, but generally, it constitutes about 45-65% of total daily calories.
Proteins: Proteins are vital for growth, repair, and maintenance of tissues. They are made up of amino acids, which are the building blocks of the body’s cells. Sources of proteins include meat, fish, dairy products, beans, and nuts. An average adult needs about 0.8 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight daily.
Fats: Fats are crucial for energy storage, hormone production, and cell membrane integrity. Healthy fats, such as those found in avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil, are essential for the body. It is recommended that fats make up about 20-35% of one’s daily caloric intake, with a focus on unsaturated fats over saturated and trans fats.
Micronutrients

Vitamins: Vitamins are organic compounds required in small amounts for various metabolic processes. Each vitamin has specific roles; for instance, vitamin C is important for immune function, while vitamin D is crucial for bone health. They are found in diverse foods such as fruits, vegetables, dairy, and lean meats. The recommended daily intake of vitamins varies widely depending on the specific vitamin.
Minerals: Minerals like calcium, potassium, and iron are inorganic elements that support numerous bodily functions, including bone formation, muscle contraction, and oxygen transport. Sources include dairy products, leafy greens, nuts, and meat. Specific intake recommendations vary for each mineral based on age, sex, and health status.
Water
Water is an often overlooked but vital component of nutrition. It supports digestion, nutrient absorption, and temperature regulation. Adequate water intake is essential for maintaining hydration and facilitating metabolic processes. The general guideline is to consume about 8 cups (64 ounces) of water daily, though individual needs may vary based on factors such as activity level and climate.
Uses of Nutrition in the Body
Nutrients play a crucial role in sustaining the body’s complex functions. Carbohydrates, for instance, are broken down into glucose, a primary energy source for cellular activities and brain function. The metabolic pathway of carbohydrates involves their conversion to glucose which is then utilized by cells for immediate energy needs or stored as glycogen in the liver and muscles for future use.
Proteins are fundamental to the body’s structure and function. They are composed of amino acids, which are essential for the synthesis of new proteins. These proteins aid in building and repairing tissues, supporting muscle growth, and producing enzymes and hormones that regulate numerous physiological processes. The body’s demand for protein can fluctuate with factors such as physical activity, injury, and overall health status.
Fats are another vital component, serving as a dense energy source and playing a key role in cellular function. They are stored in adipose tissues and utilized when the body requires additional energy. Besides energy storage, fats are also critical for maintaining healthy cell membranes, supporting brain health, and aiding in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins like A, D, E, and K.
Vitamins and minerals, though required in smaller quantities, are indispensable for maintaining health. Vitamins such as C and E function as antioxidants, protecting cells from damage. Minerals like calcium and phosphorus are essential for bone health, while iron is crucial for oxygen transport in the blood. These micronutrients support immune function, enhance metabolic efficiency, and contribute to overall well-being.
The body’s nutritional needs can vary significantly with age, activity level, and health status. For example, children and adolescents require higher amounts of certain nutrients to support growth and development. Adults may need to adjust their nutrient intake to maintain health and prevent chronic diseases, while older adults might focus on nutrients that support bone density and cardiovascular health. Similarly, athletes and individuals with specific health conditions may have unique nutritional requirements to optimize performance and manage their conditions.
Strategies for Consuming Proper Nutrition
Incorporating proper nutrition into daily life requires thoughtful planning and mindful choices. One effective strategy is meal planning. By preparing meals ahead of time, you not only save time but also ensure that your diet is balanced and nutrient-dense. Start by creating a weekly menu that includes a variety of foods from all food groups. This approach helps in maintaining a diverse diet, which is crucial for obtaining all essential nutrients.
Portion control is another key element in consuming proper nutrition. It’s essential to understand serving sizes and how much you should be eating from each food group. Using smaller plates can help manage portion sizes, and paying attention to hunger and fullness cues can prevent overeating. Including a mix of macronutrients—proteins, fats, and carbohydrates—in every meal can also aid in maintaining satiety and energy levels throughout the day.
Variety in the diet cannot be overstated. Different foods provide different nutrients, so a varied diet helps in covering all nutritional bases. Try to incorporate a rainbow of fruits and vegetables into your meals and switch up protein sources by including plant-based options like beans, lentils, and tofu alongside traditional meats and dairy.
Reading food labels is crucial for making informed dietary choices. Labels provide information on serving sizes, calories, and nutrient content, which can help you select nutrient-dense foods over those high in empty calories. Aim for foods low in added sugars, sodium, and unhealthy fats, while high in vitamins, minerals, and fiber.
Adhering to specific dietary restrictions can pose challenges, but with careful planning, they can be managed effectively. For vegetarians and vegans, ensuring adequate intake of protein, iron, and vitamin B12 is vital. Those following a gluten-free diet need to be cautious of hidden gluten in processed foods. During different life stages, such as pregnancy or elderhood, nutritional needs change. Pregnant women should focus on folic acid, iron, and calcium, while the elderly may need more vitamin D and protein to maintain bone and muscle health.
The role of supplements should not be overlooked. While a balanced diet is the best way to get nutrients, supplements can be necessary in certain situations. For example, individuals with dietary restrictions, pregnant women, or the elderly might need supplements to meet their nutritional needs. However, it is advisable to consult a healthcare provider before starting any supplement regimen.
By using this site, you agree to the Terms and conditions and Privacy Policy of https://beautyvitalityco.com/
Previous post: https://beautyvitalityco.com/brain-its-functions-and-disorders/


4 Comments
Gideon Kidd · March 28, 2025 at 1:04 pm
This is a crucial subject—keep producing such remarkable content! Someone shared their personal weight loss story, highlighting the difficulties they encountered before discovering the Diet-To-Go Meal Service. They noted that the pre-portioned meals saved them time and supported their commitment to their goals. The conversation is a reminder of how essential balance is to the weight loss journey. For those who may find it useful, here’s the link they provided.
Beauty Vitality · May 3, 2025 at 1:17 pm
You have nice taste. Stay connected for more.
Obesity: Types, Causes , Treatment | · July 19, 2024 at 11:23 pm
[…] Eating: Adopting a balanced and nutritious diet is crucial. This includes consuming plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and […]
Height Growth: 6 Methods To Increase Height - Beauty Vitality Co · August 10, 2024 at 11:10 pm
[…] Nutrition: For any human being to grow to their expected potential, they have to take balanced meals. Dietary […]