Genetics:
Genetics, therefore, is the branch of biology that focuses on the study of hereditary and genetic variation among organisms. It concerns the patterns and features that are inherited from parents to their children through genes, which are portions of DNA.
Here are some key concepts in genetics: Here are some key concepts in genetics:
1. Genes: These are the molecules of heredity consisting of DNA. The transport vesicles contain the information for protein synthesis, which is involved in the execution of several tasks within the body.
2. Chromosomes: Genes are embedded on chromosomes, which are structures found in cells that are involved in the process of transmitting hereditary traits. There are 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans, which gives a total of 46.
3. Alleles: These are two kinds of genes where one is an ‘active’ gene and the other is an inactive copy of the active gene. For example, the gene that rules over the flower color may have two alleles: red and white.
4. Genotype and Phenotype: The genotype is the singular form of genes in an organism, meaning the concrete alleles of the organism, whereas the phenotype is the appearance of the phenotype in terms of certain traits as affected by the genotype and the environment, for instance, the color of flowers or the height of plants.
5. Mendelian Genetics: This is the branch concerned with the determination of characteristics passed from one generation to the next, as postulated by Austrian-born scientist Jerrold Mendel. He got to know that characters are inherited in definite ways, and the reason he found out was that there are dominant and recessive alleles.
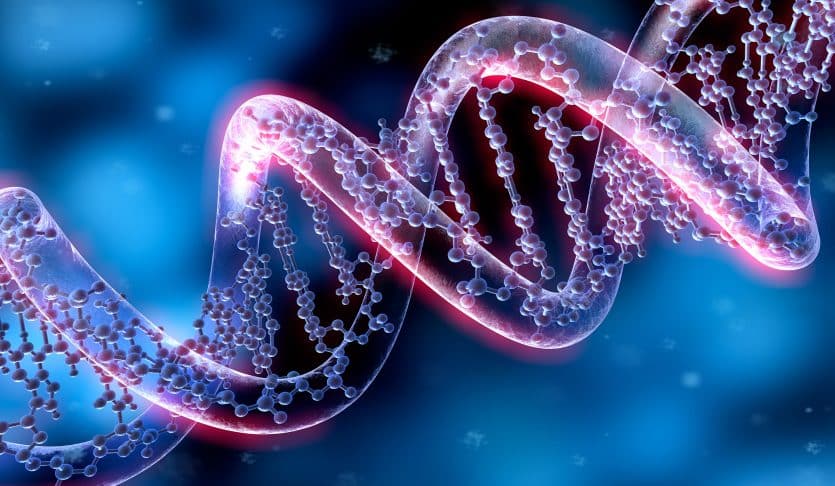
6. DNA: These are nucleic acids, one of which is deoxyribonucleic acid, which acts as the carrier of genetic information. It is a long coil made of two chains wound around each other and is a poly-nucleotide made up of nucleotide subunits that consist of a sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.
Genetics is still widely applied in different branches of science and practice, particularly in medicine, agriculture, and conservation biology, because it allows for the study of patterns of inheritance and the role of variations in the existence of living organisms.
Production Of Genetics:
Genes are produced through a procedure called DNA replication and transcription. Here’s a step-by-step explanation of how genes are formed: Here’s a step-by-step explanation of how genes are formed:
1. DNA Structure: Genes are parts of the DNA molecules, which have a two-fold long coil-like helix structure. Which includes a nitrogenous base (adenine/thymine bond or cytosine/guanine bond), a sugar, and a phosphate group all taped in a defined series, and these make a single strand of DNA.
2. Gene Location: For clarification, genes are distributed on chromosomes fixed in the cell nucleus. Anne has learned that each gene contains a unique set of bases that hold all the relevant information for the synthesis of a particular protein.
3. Transcription: The first activity that therefore has to occur when the expression of a gene is required is transcription. During this process, the DNA double helix gets split into two strands, and one of the strands provides a pattern by which an RNA strand can be built. This RNA strand is called Messenger RNA, or mRNA for short.
4. RNA Processing: Unlike prokaryotic cell RNA, the first RNA transcript of the eukaryotic cells is further processed. This process involves attaching a 5’ cap, ending with polymerase (A), and the removal of introns, leaving a mature mRNA molecule that is now ready for translation.
5. Translation: The mature mRNA is then exported out of the nucleus and into the cytoplasm to fulfill its role as a messenger RNA. Ribosomes translate the sequence of the mRNA to the codons of three bases, which signal an amino acid.
6. Protein Formation: tRNA brings the specific amino acids to the site of the ribosomes, where they are joined chained according to the code present in the mRNA molecule. This process goes on until a stop codon is read, and a whole protein is synthesized.
7. Functional Genes: Proteins, once produced, have several roles in the body and act as determinants of traits and characteristics of an individual. Therefore, the actual base sequence of a gene determines the structure and functional features of the protein that it codes for.
Conclusively, genes are synthesized through transcription and translation, encompassing steps of the synthesis of DNA sequences resulting in the formation of functional proteins.
Functions Of Genes:
It is well known that genes define the working of cells in living organisms as a result of the embodiment of the genetic code. Here’s a detailed explanation of their key functions: Here’s a detailed explanation of their key functions:
1. Protein Coding: There are just a number of important roles in cells known to be associated with genes and one of them is to code for proteins. Every gene can code for the manufacturing of a particular protein, which is significant in the construction and operations of cells. They are ubiquitous in the human body as they are required with every metabolic process, immune reactions and signal transduction among others.
2. Regulation of Biological Processes: They also participate in controlling of other activities of biological aspects. They can regulate the synthesis of a given protein and thereby control such processes such as cell division, differentiation as well as adaptation to environmental conditions.
3. Inheritance: DNA is what passes specific characteristics from one generation to another. They are given from one generation to another, and they define some of the character features, including color of the eyes, group of blood, and presence of various diseases. Such genetic information is very important in the maintenance of the species’ genes.
4. Development: While developmental process is taking place the genes determine how the tissues and organs are formed. They determine the process of cell specialization – turning into the needed types of cells and ensuring the proper functioning of an organism, which develops from a single-celled zygote.
5. Adaptation and Evolution: The genes are also required for the evolution to take place. Variants created due to mutations can cause distinctions in traits of population. It can then promote has then would favour certain traits so that the adaptations which increase chances of survival and reproduction in new environment are made.
6. Cellular Functions: In addition to that, there are genes that encode for RNA molecules with roles in regulation of activities within the cell. For instance, non-coding RNAs play a role in the regulation of gene expression and also the cellular balance.
Thereby, some main functions of genes can be outlined as follows: the code of proteins, the regulation of various biological processes, determination of the type of inheritance, the control of development, contribution to adaptation and evolution, and implementation of different cellular processes.
Significance Of Genetics:
Genes are one of the most significant supports of human body and its routine mechanism. Here’s a detailed look at their importance: Here’s a detailed look at their importance:
1. Blueprint for Proteins: Thus, genes are the blueprints for the synthesis of proteins, which are responsible for the formation as well as functioning and control elements of the body’s tissues and organs. Every Single one of them has a job; some help in constructing muscle tissue while others help in catalyzing biochemical responses.
2. Determining Traits: Therefore, genes are responsible for all the characteristics including color of hair and eye, height and other traits and tendencies such as diseases in some degree. This genetic information is passed down from parents and defines people’s genetic differences.
3. Cell Function and Maintenance: Genes are important for the proper functioning of cells, tissues, organs as well as the entire organism. They control numerous processes in cells, allowing the cells to be healthy, reproduce and communicate with the surrounding environment properly. This regulation is very important for the survival of the individual’s body since it helps to maintain the body’s balance, also known as homeostasis.
4. Development and Growth: when an individual is being developed, genes dictate what happens resulting in the formation of one or the other organs as well as systems in an individual. They orchestrate the growth from a single cell fertilized egg to a multicellular organism, make sure that all organs develop properly.
5. Response to Environment: Body acclimatisation is facilitated by genes With regard to environmental changes. They may determine how the person will cope with stress, what diet plan the person will be subscribing to or any external stressful stimulus. It shows the necessity of the adaptation for the living and wellbeing in this world.
6. Health and Disease: The genetic factors undoubtedly form the basis of one’s vulnerability to disease. There are certain risks associated with inherited genes that increase effects of diseases such as diabetes, heart diseases, or certain types of cancer. Knowledge of such problems can be used in prevention and approach to management of these genetic characteristics.
7. Evolutionary Significance: Different genes are added or substituted to one another over several generations leading to changes. They enable population’s flexibility to environmental conditions, which is paramount for the existence of species.
Thus, genes underlie human characteristics and life processes, from physical appearance and cell functions to diseases and growth. It is essential to understand that they are not limited to characterizing unique aspects but also influence general health and one’s capacity to live and prosper in various conditions.
Can Genes Get Defected?
It is true that genes can get ‘defected,’ and the term is applied more frequently to what is genetically referred to as mutations. These mutations can occur in several ways: These mutations can occur in several ways:
1. Types of Mutations:
– Point Mutations: This is changes in a number of bases in the DNA sequence but note that this may involve a one or two base change in the DNA sequence. They can be changes in the order of base pairs where one base is replaced by another, a base is added on or a base is deleted from the sequence.
– Chromosomal Mutations: These involve more extensive areas of DNA and may involve such actions as the duplication, deletion, inversion, or the shifting of portions of the chromosomes.
2. Causes of Mutations:
– Spontaneous Mutations: These, for instance, occur during DNA replication when mistakes occur or when DNA is exposed to different agents, mutations are bound to happen. At other times, the illustration or identification of mutations occurs when DNA repair functions are inoperative and cannot fix such errors.
– Environmental Factors: There are cancer causing agents, sometimes referred to as carcinogens These include radiation such UV rays, X rays, chemicals most of which are carcinogenic and viruses.
– Inherited Mutations: Others are inherited from parents to the children or one generation to the next. Any change that takes place in a germ cell which includes sperm or egg will be passed on to the next generation.
3. Effects of Mutations:
– Neutral Mutations: Some mutations even have no adverse or beneficial impact on the organisms implying that they are neutral mutations.
– Beneficial Mutations: Mutations can sometimes help, and this is why they become involved in evolution, as it is beneficial to have certain mutations in particular conditions.
– Harmful Mutations: Others can cause genetic disorder or predispose human to diseases. For instance, dependence receptor signaling genes can, when mutated be defective and lead to uncontrolled cell division leading to cancer formations.
Therefore, genes can be defected for certain reasons, and consequently, mutations that have no impact on an organism, those that would benefit the organism, or those that would harm the organism. Knowledge of these mutations is specially important for people, who are involved in genetic and evolutional sciences or develop cure for diseases.
What Happens If A Defected Genes Passes To a Child’s DNA?
If a defective gene is passed to a child’s DNA, several outcomes can occur, depending on various factors: If a defective gene is passed to a child’s DNA, several outcomes can occur, depending on various factors:
1. Genetic Disorders: If you possess a defective gene, then there is tendency of being affected by the gene related diseases. For instance if one parent is a carrier of cystic fibrosis or sickle cell anemia the child can have the disease since he or she also has the gene.
2. Carrier Status: Occasionally the gene can be mutated and yet it is not a part of any disease causing process. In this case, the child might end up being an asymptomatic carrier; the gene for the disease is passed on to the next generation but the individual may not be affected by the disease in a way that is easily noticeable. However, they could pass it on to own children or even get a copy from someone they knew.
3. Variable Expression: Possibly some mutations do not arise in every person that has the particular gene or DNA sequence. They also mean that the child could be a carrier of the mutation; however, the child shows no symptom or impact from it. This means that there is no evident action of the gene, meaning that it will not in any way manifest its presence in the body.
4. Potential Benefits: Of course, not infrequently, a defective gene can be beneficial in some ways or another. For instance, certain genetic variations that predispose a person to the disease may have advantages in certain conditions.
Therefore, the possible consequences of the defect of a gene on a child’s DNA can range from severe to insignificant depending on genetic transmission and environmental stimuli.
By using this site, you agree to the Terms and conditions and Privacy Policy of https://beautyvitalityco.com/
Previous post: https://beautyvitalityco.com/height-growth-6-methods-to-increase-height/



1 Comment
Pituitary Gland- BVC1 - Beauty Vitality Co · August 15, 2024 at 1:59 pm
[…] Previous post: https://beautyvitalityco.com/genetics/ […]